Shipping criterion for Higashine Cherries
We have determined the shipping and cultivation criteria to protect the Higashine Cherry brand. Higashine Cherries are cultivated in Higashine City and select areas in neighboring cities and towns. These cherries must meet strict color grade and size criteria (as listed below) before they are shipped. By choosing Higashine Cherries, you are guaranteed cherries of the highest quality.
Cherries that fail to meet standard shipping specifications cannot be labeled as Higashine Cherries.

Color-based Classification Standard
The color-based classification standard plays a crucial role in ensuring quality assurance.
“Higashine Fruit Kingdom” Fruits Industrial Cluster Association has established shipping standards based on color to ensure that consumers receive high-quality cherries.
To qualify for shipping under the Higashine Cherry label, the color ratio standard requires that more than 70% of the surface area must be colored for Sato Nishiki Cherries and more than 75% for Benishuho Cherries.




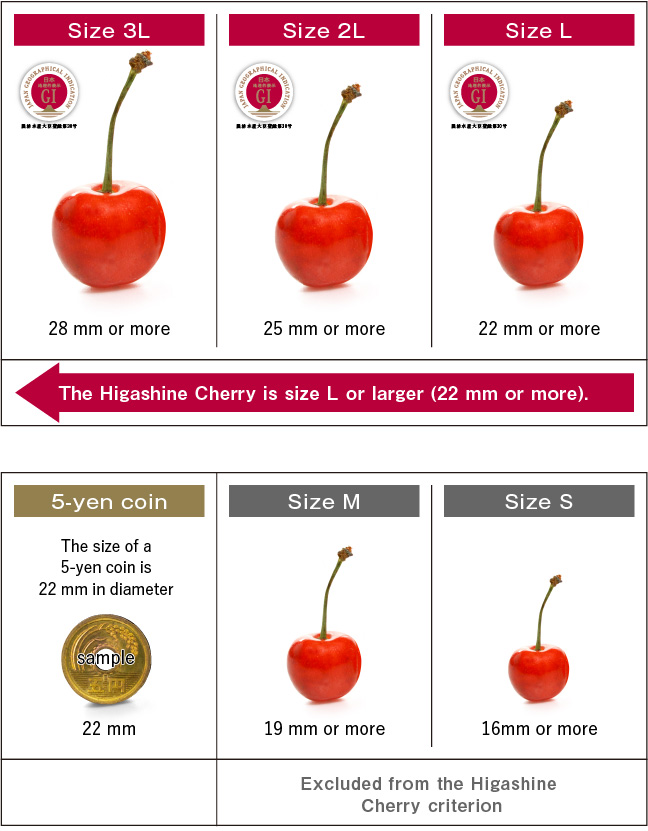
Cherry size determined by diameter
The cherry size is determined by diameter, not weight.
Harvested cherries are sorted by their quality one cherry after another. Cherries are sorted by the colored area criterion and by their sizes with a plate that is called a criterion plate and has holes of all sizes. Yamagata Prefecture decides that the diameters of cherries to be shipped as fresh cherries to be eaten raw are size M (19 mm) or more, but only size L (22 mm) or more of cherries are shipped as Higashine Cherries. The diameter is the same as a 5-yen coin.

Cultivation criterion for Higashine Cherries

We shall endeavor to observe the following in Higashine Cherry cultivation:
① The planting quantity shall be 10 to 15 trees per 10 ares in the garden.
② Cultivation shall use Weather Protection Facilities to protect fruit from cracking.
③ Nets that protect fruit from birds shall be stretched over the side of Weather Protection Facilities to protect fruits from wild birds.
④ Reflection sheets shall be placed under trees to promote fruit coloration.
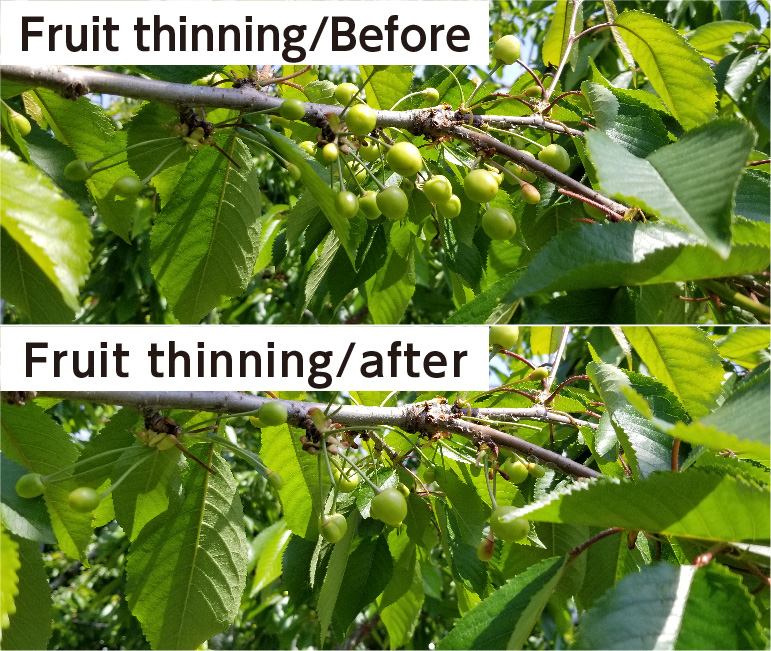
⑤ Disbudding, fruit thinning and leaf thinning shall be conducted to promote fruit enlargement.
To the shipment of Higashine Cherries
Cherry production calendar (products cultivated in open ground)
(Average working time is about 8 hours per tree)
Place reflective material under trees (making the part exposed to sunlight larger is effective for promoting fruit coloration)









